exploding battery: how it works 2
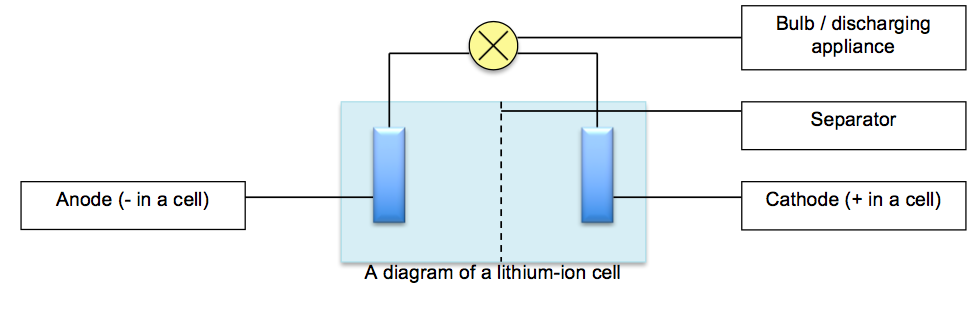
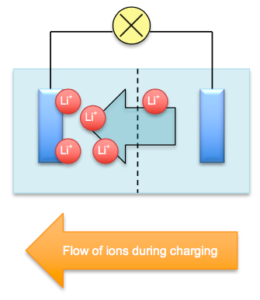
Topic: O Level Secondary 4: Electrolysis and Electric Cells, Reaction Enthalpy, Exploding phone batteries In 2016, one of the biggest tech news was the recall of Samsung Note 7 phones because some phones exploded during charging. Why did this happen? Background To make phones lighter, one common battery model is the lithium battery (lowest molecular mass amongst metals), which works by the movement of lithium ions from one electrode to another during the charging and discharging process.
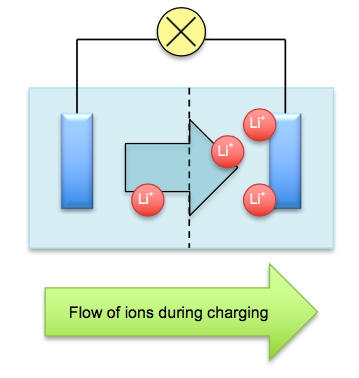
The cathode and anode are separated by an organic liquid called an electrolyte filled with mobile ions and a porous material called the separator that separates the electrodes from touching. An electrolyte is a liquid which conducts electricity by the movement of mobile ions. When the batteries are charged, electricity drives the lithium ions from the cathode, across an ion-filled electrolyte fluid, and into the anode, which is made of stacks of graphite. As the battery drains, for example when you are watching a YouTube video, the lithium ions return from the anode back into the cathode. This is known as the discharging process.
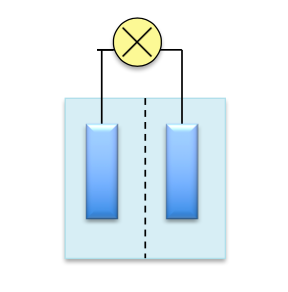
What could have happened for the exploding batteries? As part of a manufacturing feat to make the phone thinner and charging faster, it could be the electrodes are placed too close together:
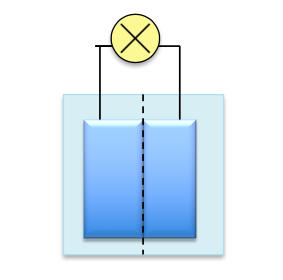
So what really caused these exploding batteries? During charging the electrodes expand upon heating, unfortunately causing them to touch one another. Instead of ions transferring from one electrode to another, the direct contact cause electrons to move from electrode to electrode, causing a short circuit. This is one possible explanation for the exploding batteries.
This short circuit mean that the current running through the phone is very high, which results in overheating. This overheating cause neighbouring cells’ electrodes to expand, touch and cause more short circuits. This domino effect of cells malfunctioning is called thermal runaway. During thermal runaway, the miniature battery modules melt, give off heat, and the electrolyte material between the anode and the cathode may even boil. The heat produced by the short circuit can cause the electrolyte to react further, which can produce gaseous compounds, and the build-up in pressure likely causing the battery to explode. Are most lithium battery safe then? Every battery is basically a packet to store and release energy, and unsafe practices like overheating the phone are the more likely the cause of explosions than the type of batteries. Hence, it is always wiser to take precautionary measures to stop phone usage or charging if you feel the phone is heating too quickly and warmer than normal usage. As such, be careful when you charge your phones to avoid exploding batteries!
Seb Academy offers a comprehensive O Levels, IP Program and A Levels Program to help you achieve the best score you can, for your results towards your examinations at the O Levels, Sec 4 IP graduation examinations and A levels. Join us to gain more insights and add the latest Chemistry insights in news, such as this study on exploding batteries, to our repertoire of academic knowledge while developing a curiosity and appreciation for the subject!